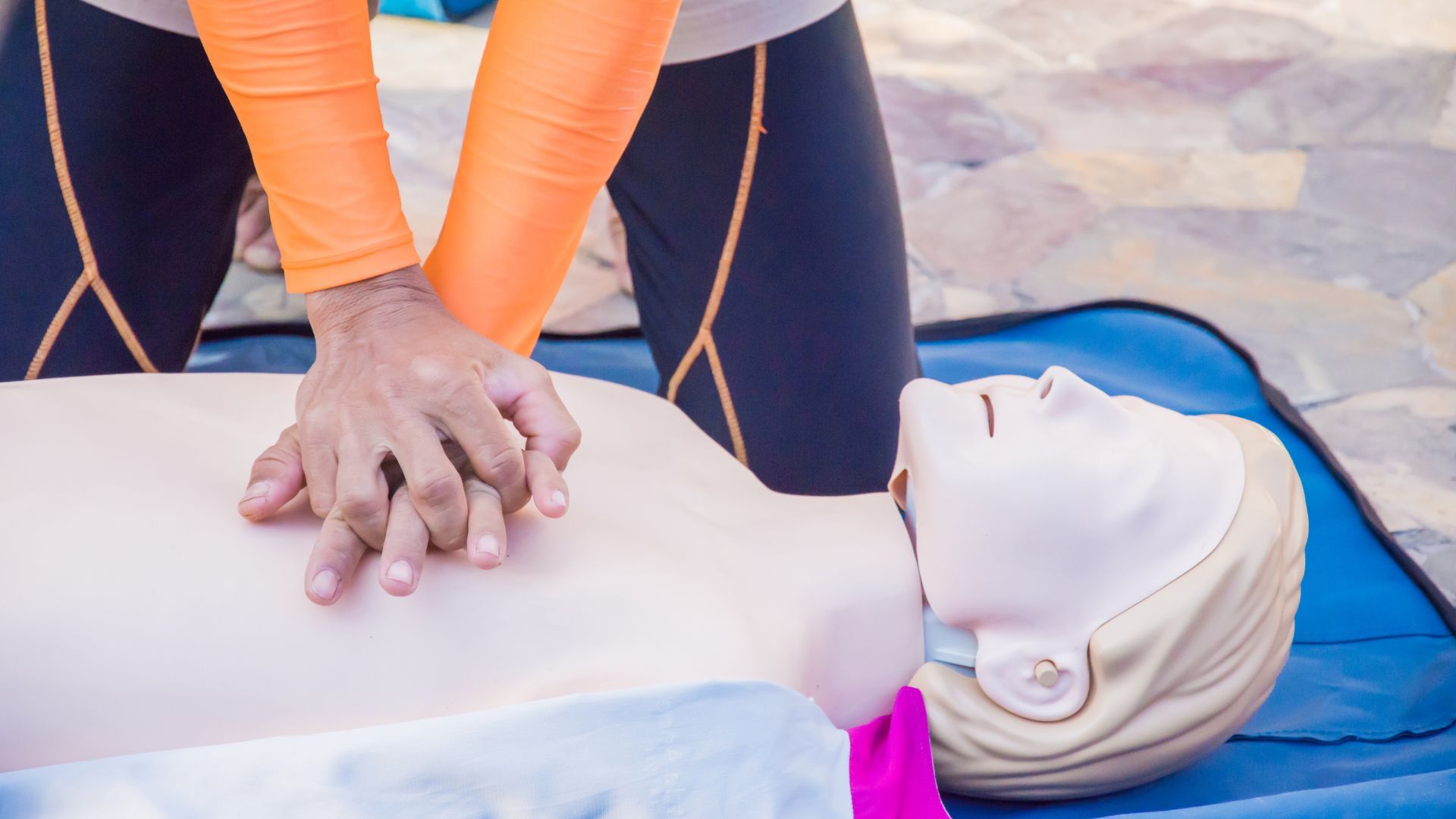
Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR
Contents
Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR Pronunciation: Si-mult-ta-ne-ous Ven-til-a-tion Com-pres-sion C-P-R (sɪˌmʌltəˈneɪəs vɛntɪˈleɪʃən kɒmprɛˈʃən sē-pē-är)
Definition: Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR (SVC-CPR) is a method of cardiopulmonary resuscitation that involves providing chest compressions and ventilations at the same time, rather than alternating between the two as in traditional CPR. The goal is to increase blood flow and oxygen delivery to the heart and brain.
What is Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR?
Overview:
SVC-CPR is a newer approach to CPR that aims to enhance the effectiveness of resuscitation efforts by eliminating the pauses between chest compressions and ventilations, maintaining more consistent pressure in the chest and thereby promoting blood flow to vital organs.
Key Facts about Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR:
- Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR can enhance blood flow to the heart and brain during a cardiac arrest, potentially increasing the chance of survival.
- Implementing SVC-CPR requires precise coordination and may not be suitable for untrained bystanders. It is typically used by healthcare professionals.
- Studies are ongoing to further evaluate the effectiveness of SVC-CPR compared to traditional CPR.
Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR Implementation
How is Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR performed?
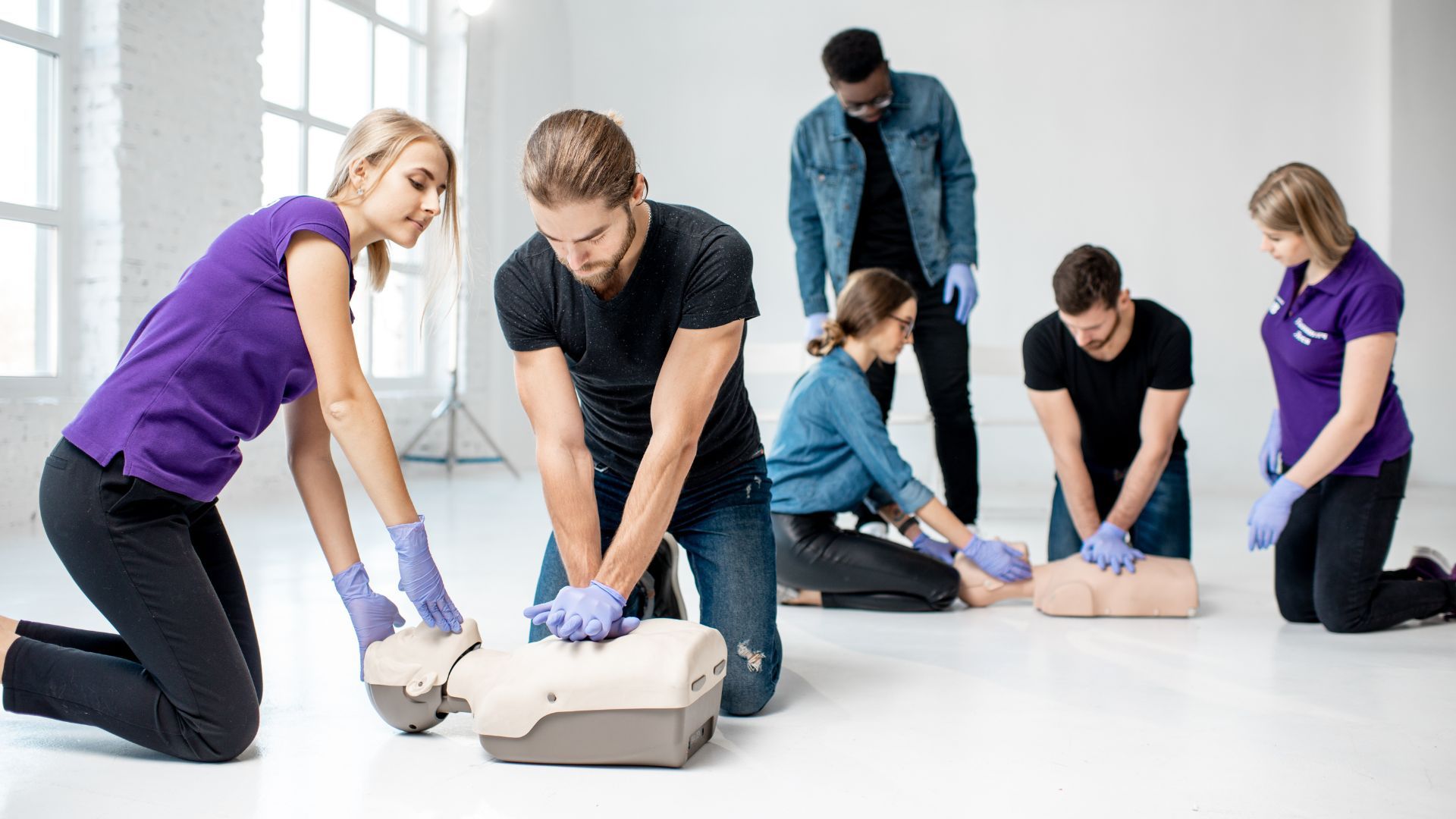
SVC-CPR is performed with careful timing and coordination:
- One rescuer provides continuous chest compressions.
- A second rescuer provides ventilations without pausing the compressions.
- Both actions should be coordinated so that ventilations occur during the upward phase of compressions.
Frequently Asked Questions About Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR
What are the benefits of Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR?
Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR helps to maintain pressure within the chest, which can enhance blood flow to the heart and brain during a cardiac arrest. This could potentially improve outcomes.
Who can perform Simultaneous Ventilation-Compression CPR?
SVC-CPR requires a high level of coordination and is typically performed by healthcare professionals. More research and training materials are needed for wider adoption.
References:
- American Heart Association. (n.d.). CPR & ECC Guidelines. Retrieved July 26, 2023, from https://cpr.heart.org/en/resuscitation-science/cpr-and-ecc-guidelines
- Wikipedia. (n.d.). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Retrieved July 26, 2023, from https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Cardiopulmonary_resuscitation
More Articles