Rescue Breathing
Contents
Rescue Breathing Pronunciation: Res-cue Breath-ing (ˈresˌkyo͞o ˈbrēT͟HiNG)
Definition: Rescue breathing, also known as artificial respiration, is a procedure that involves breathing for an unconscious person who has stopped breathing or is not breathing adequately, with the aim of oxygenating their blood and maintaining life until further medical help arrives.
What is Rescue Breathing?
Overview:
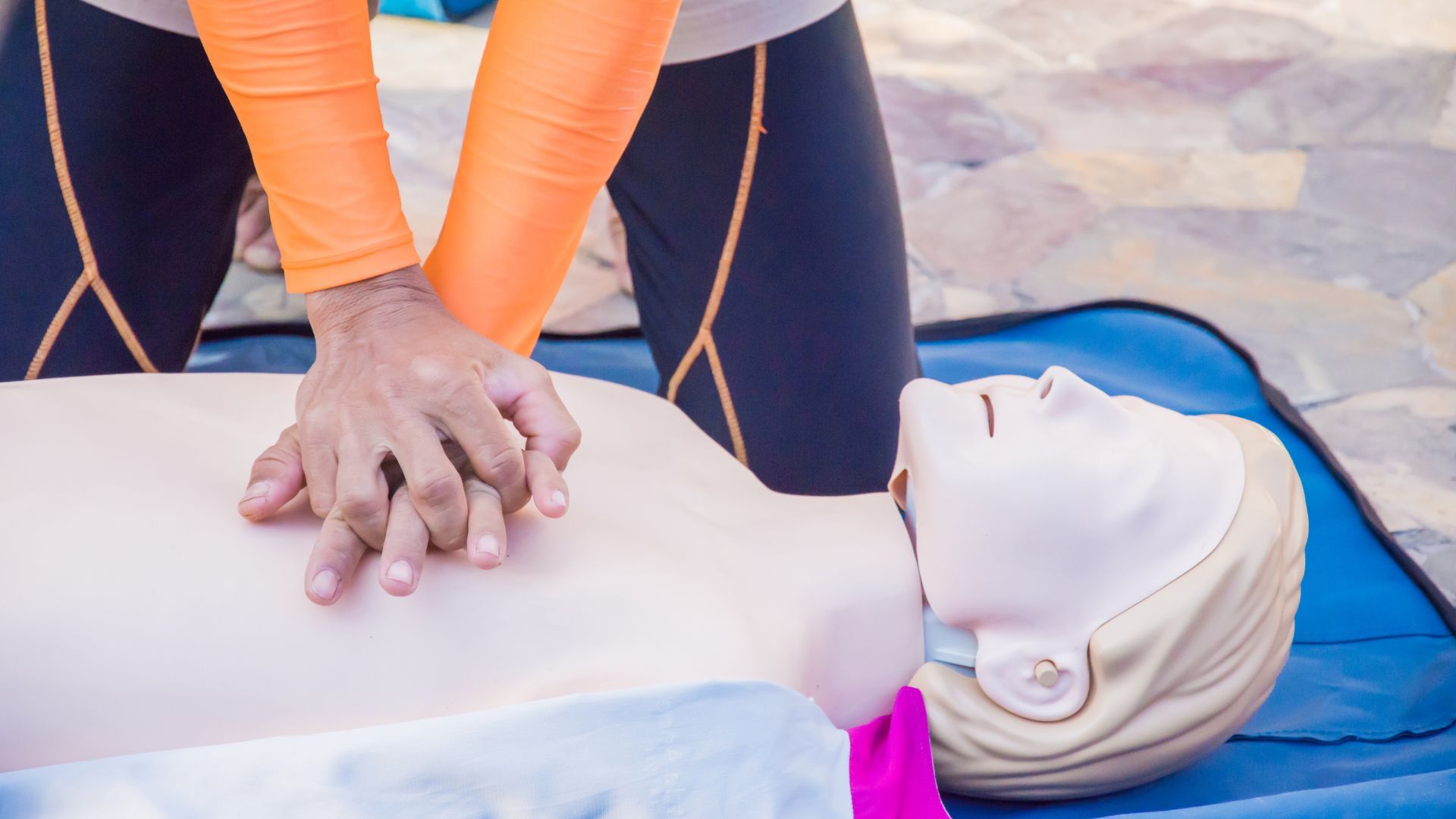
Rescue breathing is a critical component of basic life support in situations where a person’s breathing is inadequate or has stopped. It involves giving breaths directly into the person’s mouth and can be a lifesaving measure until more advanced care can be given.
Key Facts about Rescue Breathing:
- Rescue breathing is used when a person is not breathing or breathing insufficiently but has a pulse.
- It involves tilting the person’s head back, lifting the chin, pinching the nose, and breathing into the mouth.
- The rescuer should give 1 breath every 5 to 6 seconds, or about 10 to 12 breaths per minute for an adult.
- Each breath should be enough to make the chest rise but no more.
- The person’s pulse and breathing should be checked regularly while performing rescue breathing.
Rescue Breathing Usage & Understanding
How to perform Rescue Breathing?
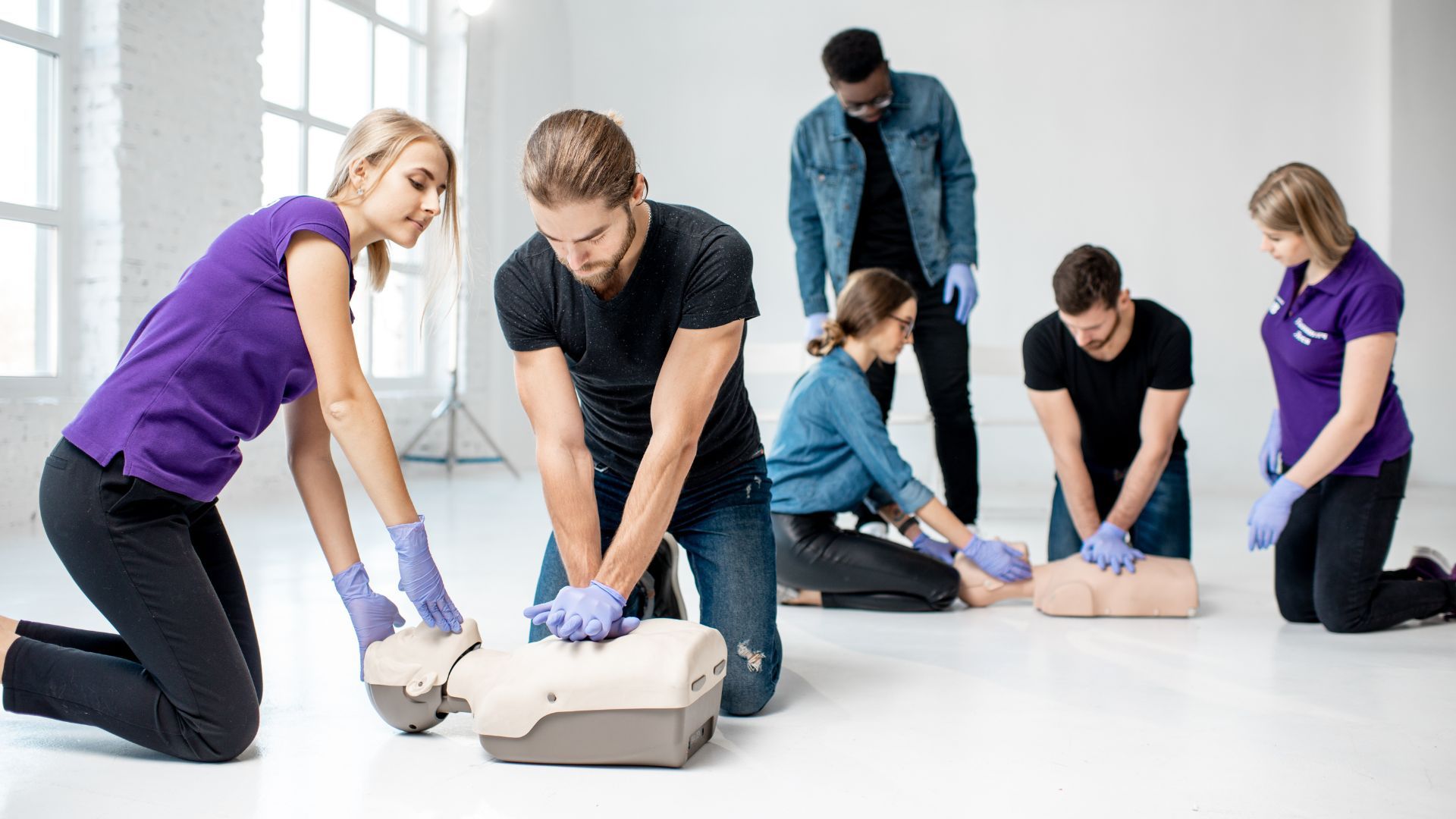
Here are the basic steps to perform rescue breathing on someone:
- Open the person’s airway by tilting the head and lifting the chin.
- Check for breathing: Look, listen, and feel for no more than 10 seconds.
- If the person is not breathing or is breathing ineffectively, pinch their nose shut.
- Take a normal breath, cover the person’s mouth with yours to create an airtight seal, and give 2 one-second breaths as you watch for the chest to rise.
- Continue rescue breathing, giving 1 breath every 5 to 6 seconds.
Frequently Asked Questions About Rescue Breathing
When should Rescue Breathing be performed?
Rescue Breathing should be performed when a person is not breathing or is breathing ineffectively but still has a pulse. If a pulse cannot be detected, CPR (which includes chest compressions and rescue breaths) should be performed.
What is the difference between Rescue Breathing and CPR?
Rescue breathing is performed when a person has a pulse but is not breathing adequately, while CPR (cardiopulmonary resuscitation) is performed when a person does not have a pulse, and includes both chest compressions and rescue breaths.
References:
- Mayo Clinic. (n.d.). Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR): First aid. Retrieved July 25, 2023, from https://www.mayoclinic.org/first-aid/first-aid-cpr/basics/art-20056600
- MedlinePlus. (n.d.). Breathing – slowed or stopped. Retrieved July 25, 2023, from https://medlineplus.gov/ency/article/000047.htm
More Articles