Lay Rescuer
Lay Rescuer
Pronunciation: LAY REZ-kyoo-er
Definition:
A lay rescuer is an individual who is not formally trained in advanced medical procedures but may have received basic training in first aid, cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR), and the use of automated external defibrillators (AEDs). They are non-professionals who provide immediate care in emergency situations until professional help arrives.
What is a Lay Rescuer?
Overview:
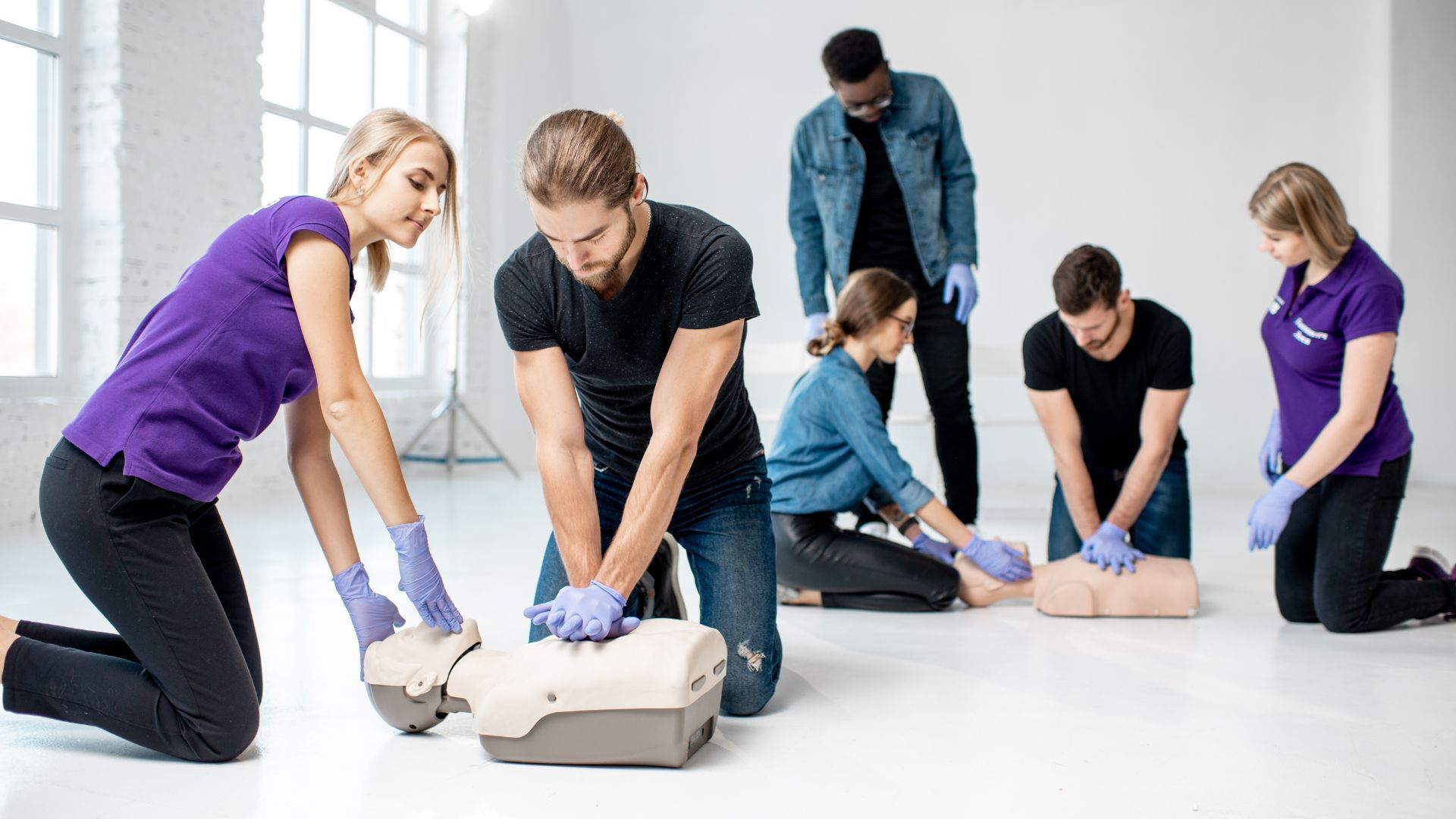
Lay rescuers play a pivotal role in the early stages of emergencies, as they are often the first to respond on the scene. Their primary goal is to stabilize and support the victim until professional medical personnel can take over.
Key Facts About Lay Rescuers:
- They may be trained in basic life-saving techniques like CPR and AED usage.
- Can make a significant difference in outcomes, especially in cardiac arrest situations where timely intervention is crucial.
- Are often bystanders, family members, teachers, coaches, and coworkers.
Lay Rescuer | Symptoms & Causes
In what scenarios might a Lay Rescuer intervene?
Lay rescuers can act in:
- Cardiac arrest events.
- Choking incidents.
- Drowning situations.
- Basic wound care.
- Initial stages of trauma or accidents.
What prompts a Lay Rescuer to act?
Triggers include:
- Recognizing someone is in distress or unresponsive.
- Witnessing an accident or fall.
- Observing signs of choking or respiratory distress.
- Being nearby when someone collapses.
How does a Lay Rescuer assess situations?
Assessment by lay rescuers often involves:
- Scene safety: Ensuring the environment is safe for both the victim and the rescuer.
- Checking responsiveness: Shouting and tapping the victim to see if they react.
- Calling for help: Immediately alerting emergency services.
What are the common interventions performed by Lay Rescuers?
Interventions include:
- CPR: Chest compressions and rescue breaths for victims in cardiac arrest.
- AED usage: If available, applying and using the automated external defibrillator as instructed.
- Heimlich Maneuver: For choking victims.
- Basic first aid: Addressing minor injuries or bleeding.
More Articles