Emergency Cardiovascular Care (ECC)
Contents
ECC (Emergency Cardiovascular Care)
Pronunciation: E-C-C
Definition:
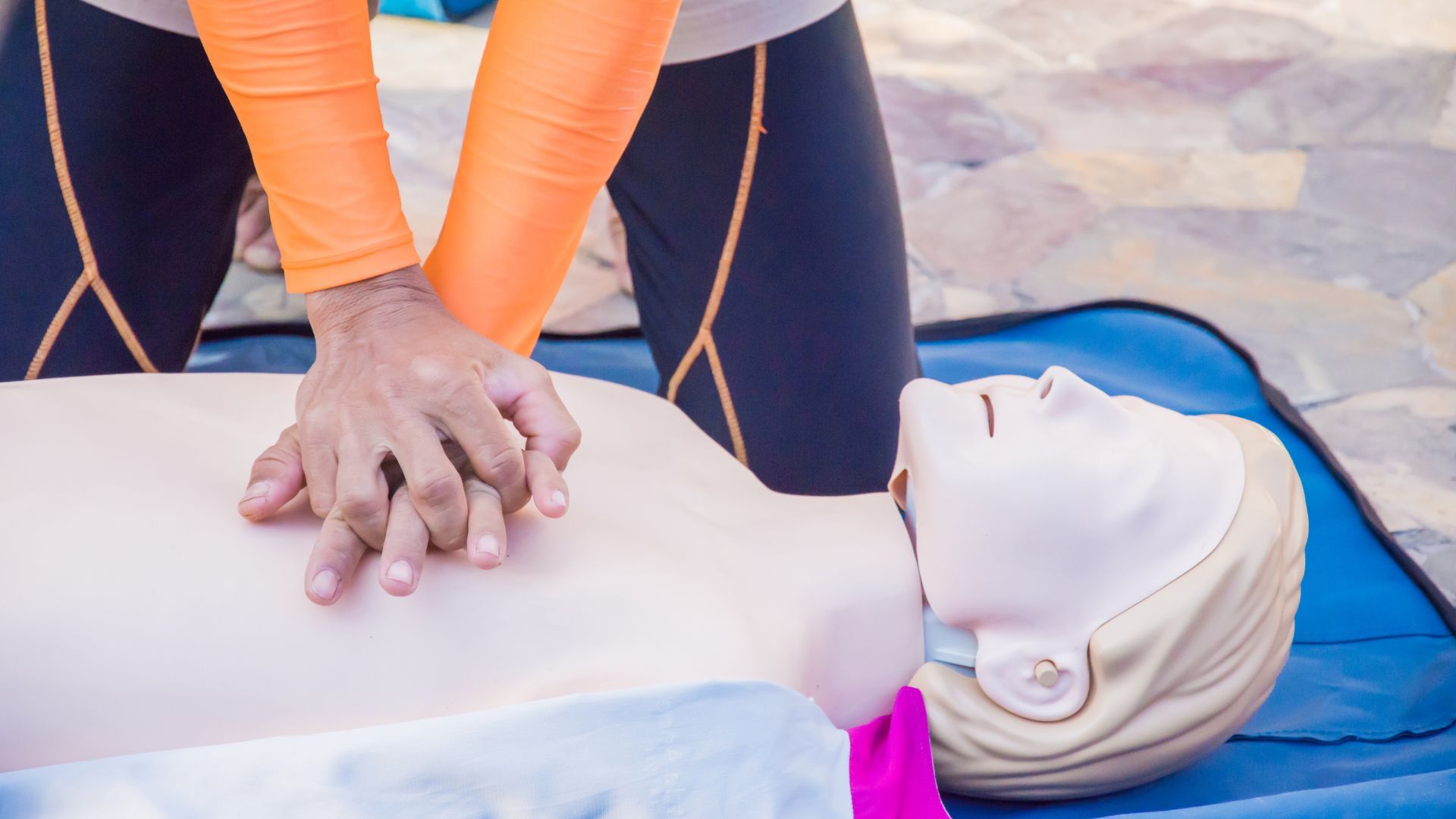
ECC stands for Emergency Cardiovascular Care. It refers to the immediate and essential actions taken to treat life-threatening cardiac conditions, particularly sudden cardiac arrest, and encompasses a range of interventions from basic cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) to advanced cardiac life support.
What is ECC?
Overview:
Emergency Cardiovascular Care represents a series of interventions designed to restore circulation and breathing in patients experiencing cardiac emergencies. Prompt ECC can significantly improve the chances of survival and reduce the risk of long-term neurological and cardiac damage.
Key Facts About ECC:
- Time is a crucial factor in ECC; the sooner it’s started, the better the patient’s outcome.
- ECC includes procedures like CPR, defibrillation, and advanced airway management.
- The American Heart Association and other global organizations regularly release guidelines on best practices in ECC.
Why might someone need ECC?
ECC is necessary for conditions such as:
- Sudden cardiac arrest.
- Severe arrhythmias like ventricular fibrillation (VF) or ventricular tachycardia (VT).
- Severe choking where the airway becomes blocked.
- Drowning or other instances of asphyxia.
What precipitates the need for ECC?
Factors leading to cardiovascular emergencies include coronary artery disease, electrolyte imbalances, trauma, respiratory failure, and drug overdose, among others.
How is the need for ECC determined?
- Assessment: Rapid evaluation of breathing, pulse, and responsiveness.
- Use of Automated External Defibrillators (AEDs): AEDs can analyze a patient’s heart rhythm and recommend if defibrillation is needed.
- Monitoring: Advanced tools, like electrocardiograms (ECGs), may be used by healthcare professionals to determine the cardiac condition.
What interventions are included in ECC?
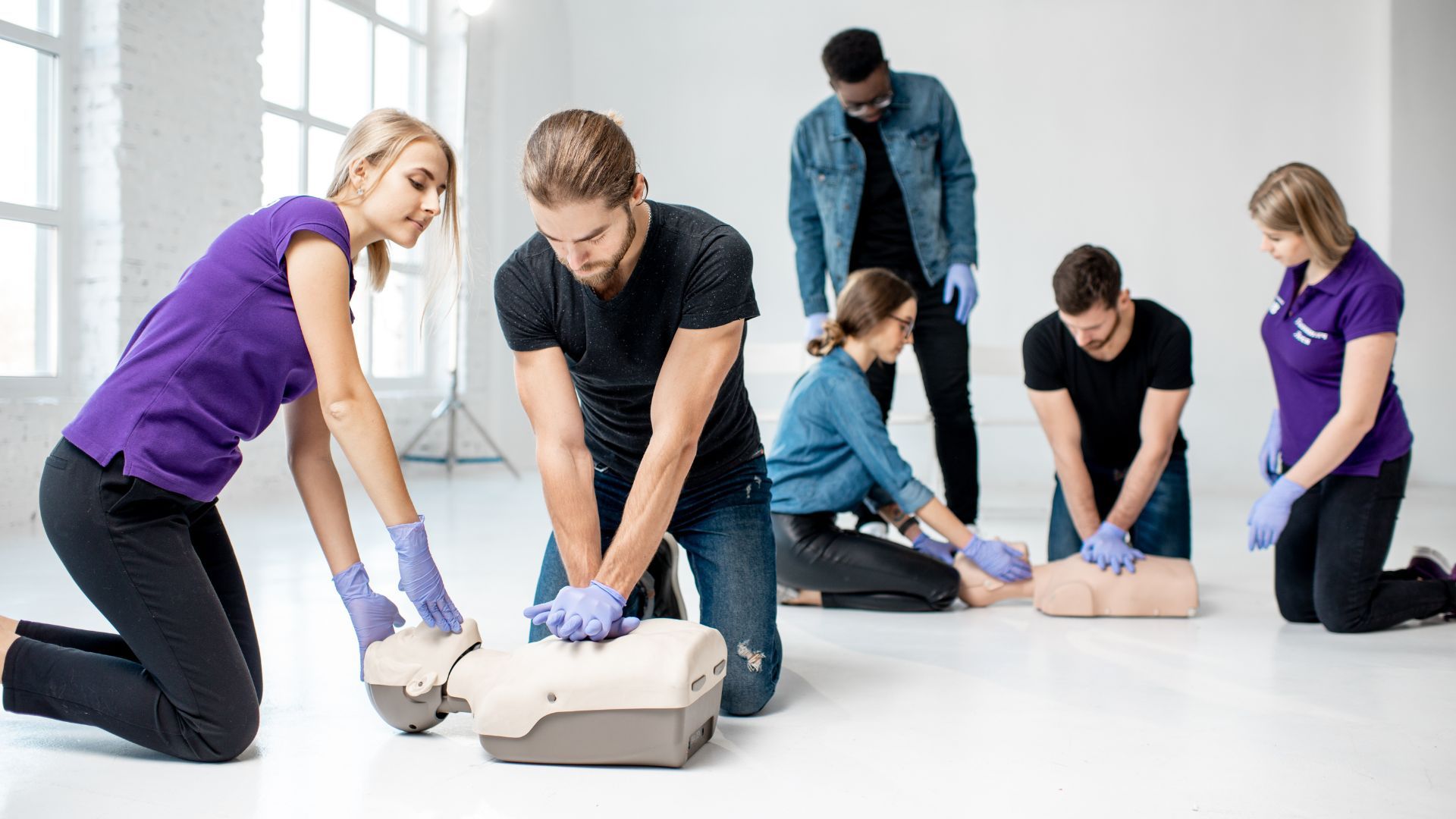
- Basic Life Support (BLS): Initial response like checking for responsiveness, calling for help, and starting CPR.
- Defibrillation: Using electrical shocks to restore normal heart rhythm.
- Advanced Cardiac Life Support (ACLS): Includes advanced airway management, drug administration, and rhythm analysis.
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care: After return of spontaneous circulation, care focuses on stabilizing the patient and identifying the cause of the arrest.
More Articles