What is Cardiac Chain of Survival
Cardiac Chain of Survival Pronunciation: ˈkär-dē-ak ˈchān əv sər-ˈvī-vəl
Definition: The Cardiac Chain of Survival is a series of critical steps that, when followed in a timely manner, can significantly improve the chances of survival for someone experiencing a cardiac arrest. These steps are designed to provide rapid and efficient care, helping to restore blood flow to the heart and brain as quickly as possible.
Frequently Asked Questions About Cardiac Chain of Survival
What are the steps in the Cardiac Chain of Survival?
The Cardiac Chain of Survival consists of the following steps:
- Early Recognition and Call for Help: Quickly recognizing the signs of cardiac arrest and immediately calling 911 or your local emergency number.
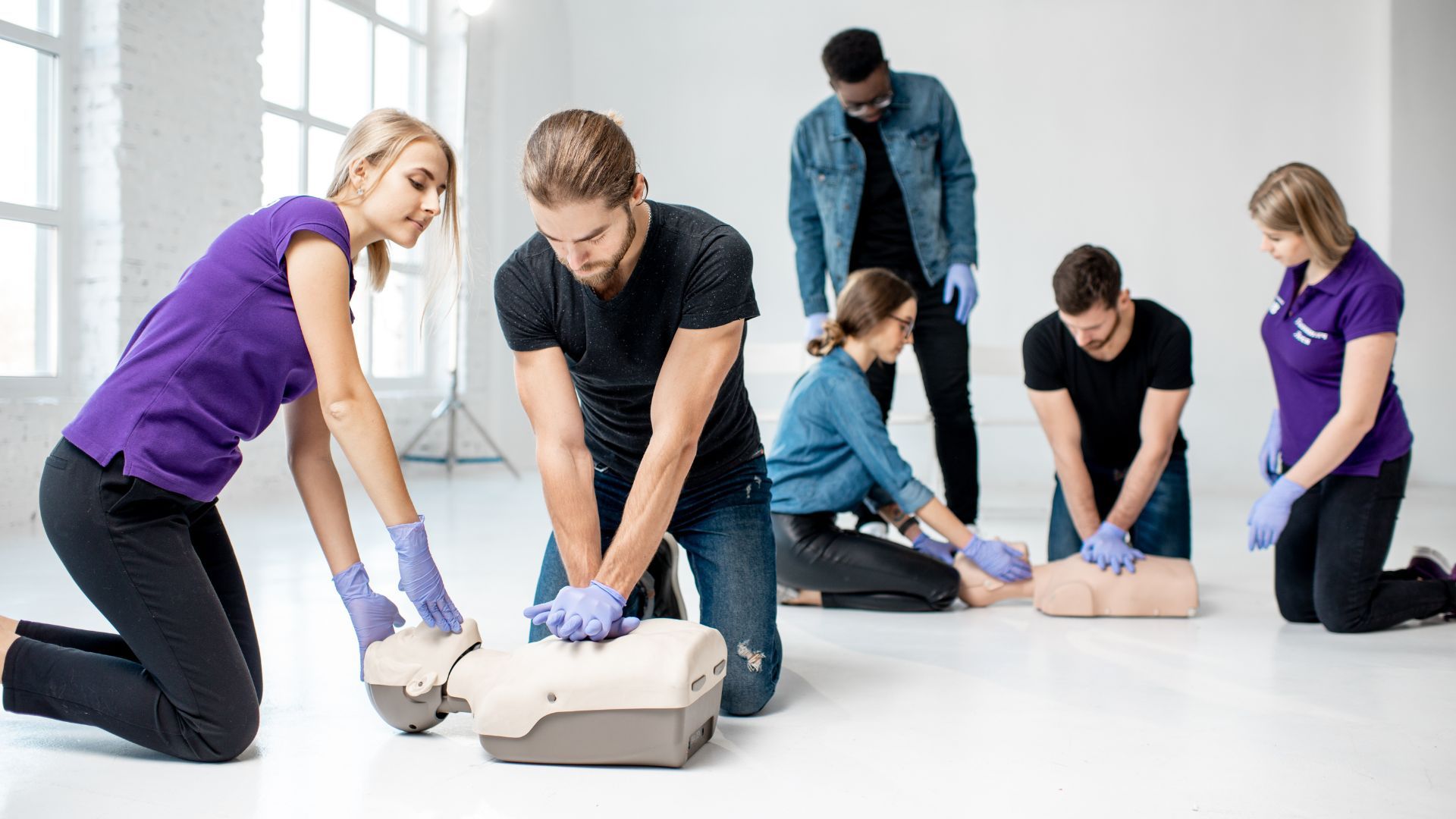
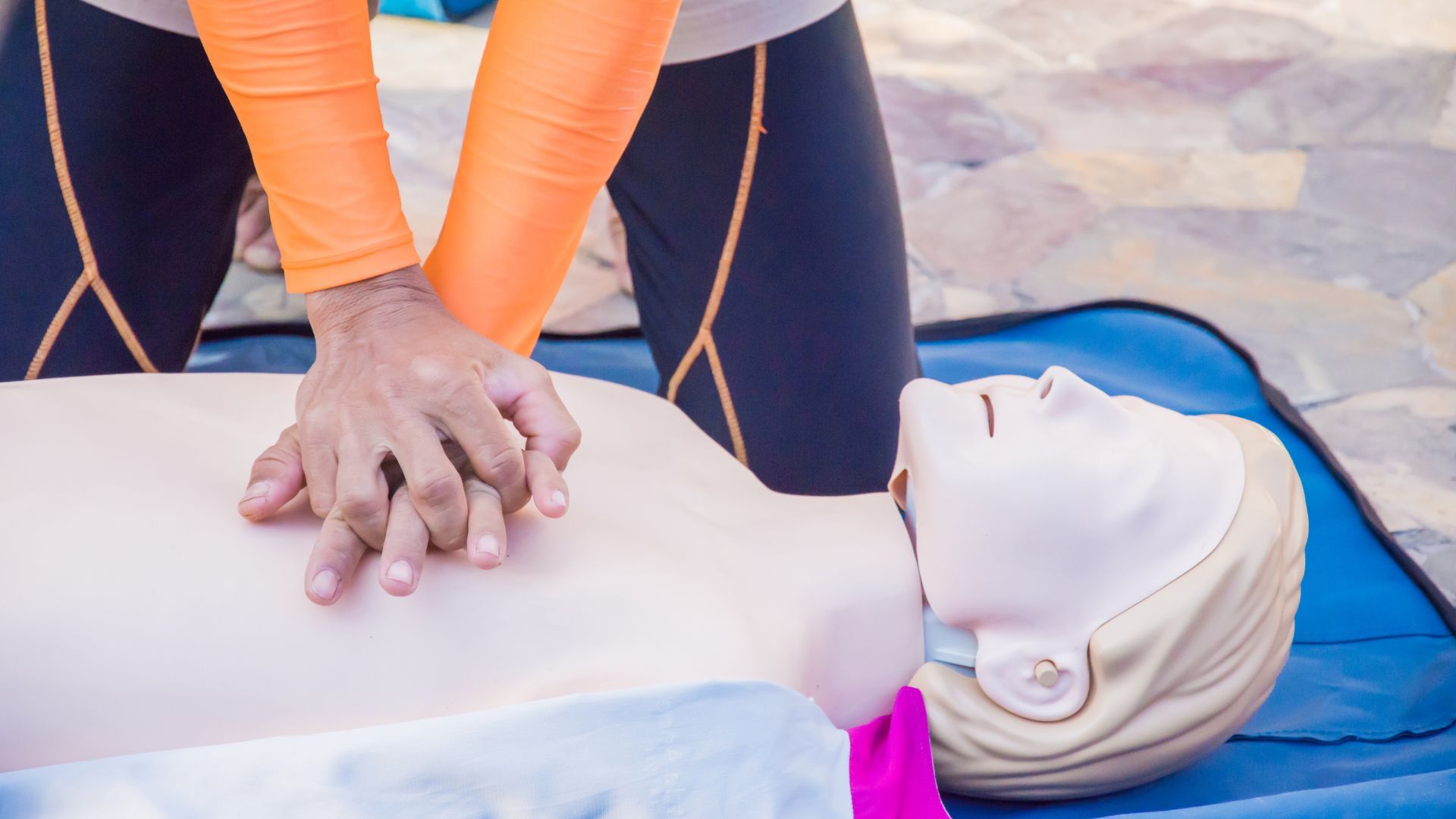
- Early CPR: Initiating Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation (CPR) as soon as possible, with an emphasis on high-quality chest compressions.
- Early Defibrillation: Using an Automated External Defibrillator (AED) to deliver an electric shock to the heart, if needed, in order to restore a normal rhythm.
- Early Advanced Life Support: Rapid arrival and intervention by emergency medical service (EMS) personnel to provide advanced care, including airway management, medications, and advanced cardiac life support (ACLS) measures.
- Post-Cardiac Arrest Care: Providing comprehensive care in a healthcare facility, including targeted temperature management, optimization of hemodynamic and respiratory support, and neurological assessment and support.
Why is the Cardiac Chain of Survival important?
The Cardiac Chain of Survival is important because it highlights the critical interventions that can significantly increase the chances of survival and recovery for someone experiencing cardiac arrest. Following these steps in a timely manner can help save lives and reduce the risk of long-term neurological damage.
How can I contribute to the Cardiac Chain of Survival?
You can contribute to the Cardiac Chain of Survival by:
- Learning to recognize the signs of cardiac arrest.
- Knowing how to call for help in an emergency situation.
- Getting trained in CPR and AED use, and renewing your skills regularly.
- Advocating for increased public access to AEDs in your community.
- Sharing information about the Cardiac Chain of Survival with friends, family, and colleagues to raise awareness.
More Articles